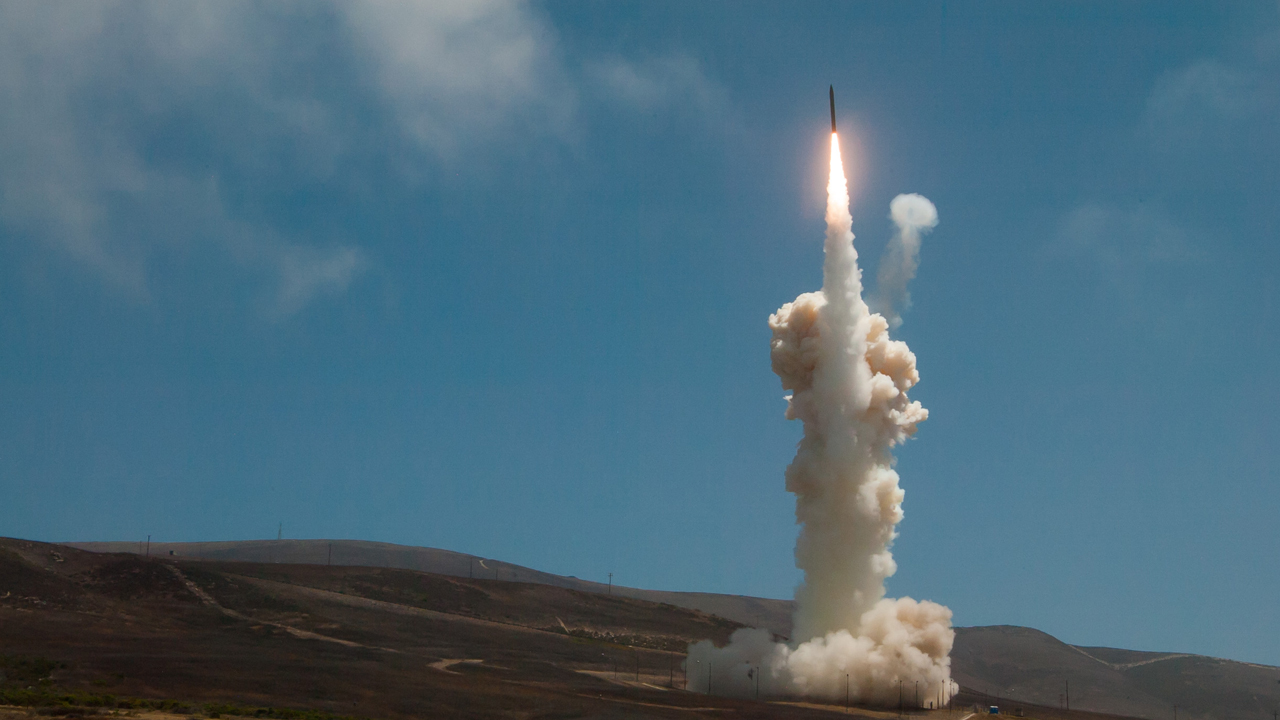
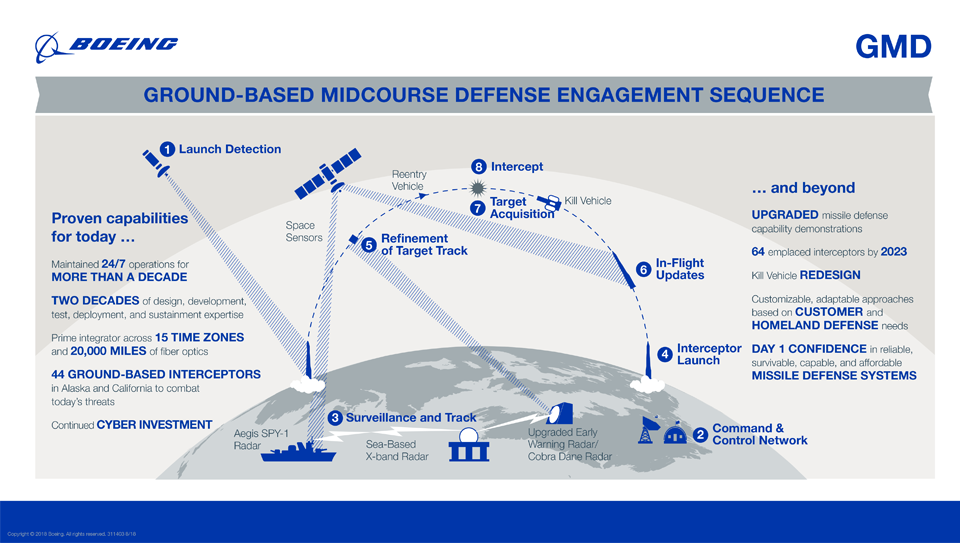
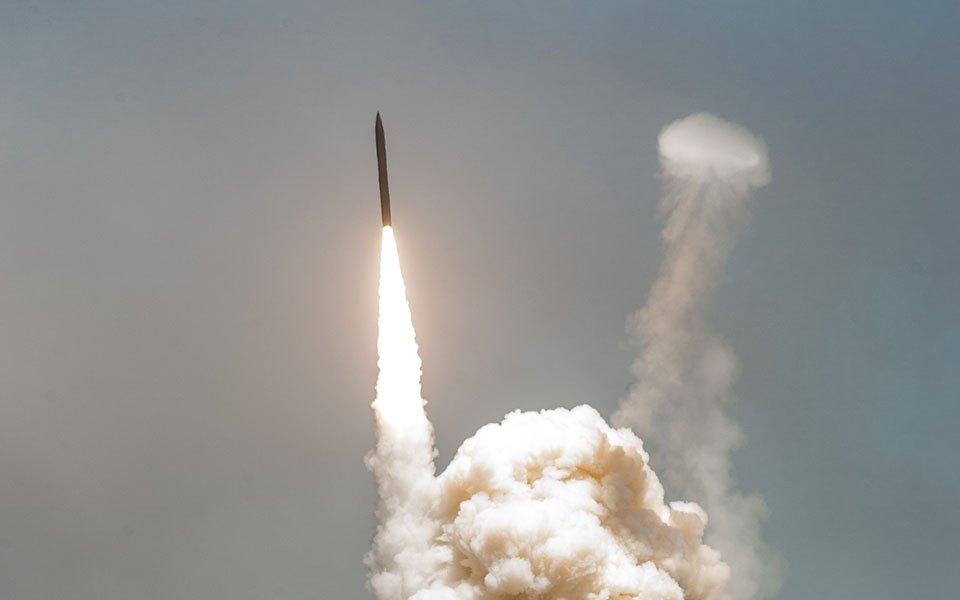
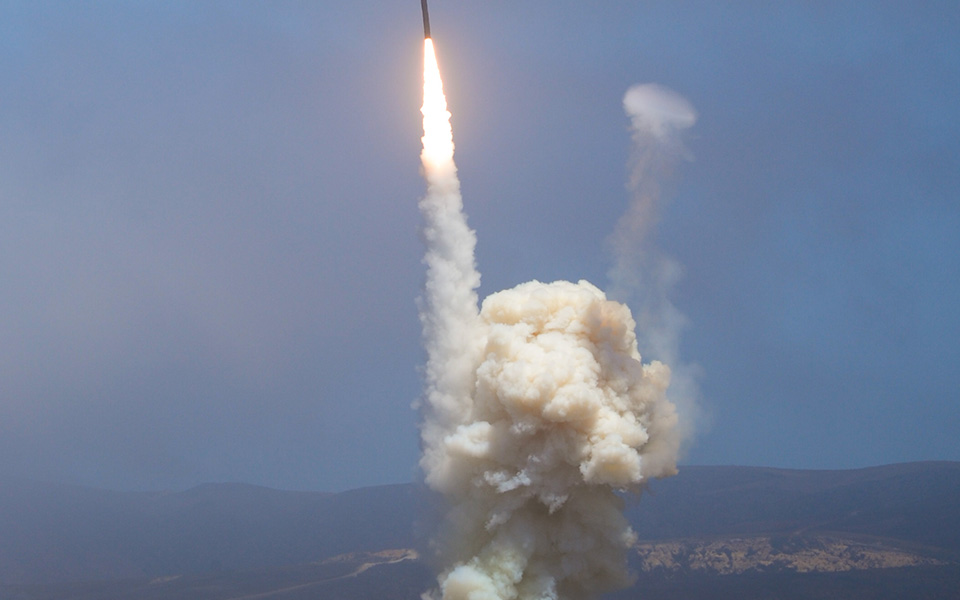
The Ground-based Midcourse Defense (GMD) system is the United States' only operationally deployed missile defense program capable of defending the entire U.S. homeland (including Alaska and Hawaii) against long-range ballistic missile attacks. GMD is designed to detect, intercept and destroy long-range ballistic missiles during their midcourse phase of flight. The system provides early detection and tracking during the boost and midcourse phase, as well as target discrimination, precision intercept and destruction of the target through force of collision. GMD is an integral element of the U.S. Missile Defense Agency's layered ballistic missile defense architecture. As prime contractor, Boeing designs, produces, integrates, tests and sustains all GMD components deployed across 15 time zones.
Ground-based Midcourse Defense (GMD)
America's Homeland Defense Shield
GMD Program Milestones
Ground-Based Midcourse Defense System Gallery








- Image 01
- Image 02
- Image 03
- Image 04
- Image 05
- Image 06
- Image 07
- Image 08
- Image 09
- Image 10
Ground-based Midcourse Defense Customer
Boeing has helped the United States Missile Defense Agency guard against all missile threats through its Ground-based Midcourse Defense system, which became operational in 2004. Boeing has been the lead for the capability since 1998.

Ground-based Midcourse Defense Feature Stories
Ground-based Midcourse Defense Quick Facts
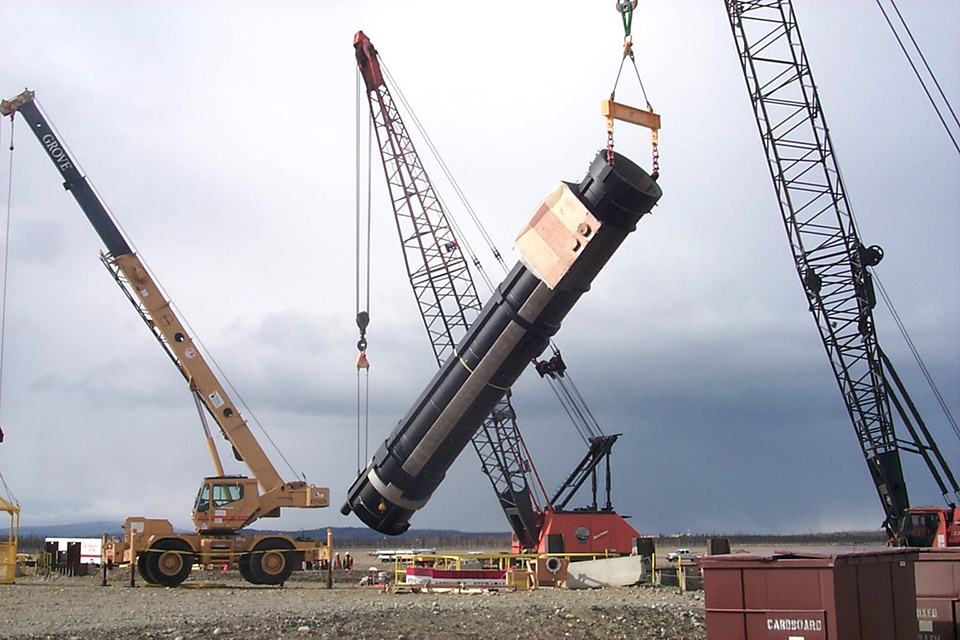
- Interceptors are emplaced at two sites in the United States, one in Vandenberg, Calif., and the other in Fort Greely, Alaska.
- Altogether, the Ground-based Midcourse Defense system requires 20,000 miles (32,187 kilometers) of fiber optic cable.
- Boeing has been prime contractor since 1998.
- Boeing has partnered with the U.S. Missile Defense Agency in the design, development, integration, test and sustainment of all GMD components.
- Key subcontractors include Northrop Grumman and Raytheon.